|
Dog Bite Infections
These are some of the infections which may occur if the dog bite is left untreated.
|
Dog Bite Antibiotics
Not all dog wounds may require antibiotics. Statistics shows that approximately 15 to 20 percent of dog bite wounds become infected. Some dog bite wounds which are more prone to infection are: puncture wounds, crush injuries and hand wounds have a greater chance of becoming infected than tears or scratches. These infections carry bacterial orgasms called poly-microbial organisms. This infection is treated with prophylactic antibiotics. The treatment of the wound with antibiotics has an average antibiotic intake of three to seven days. |
What To Do If Bitten By A Dog
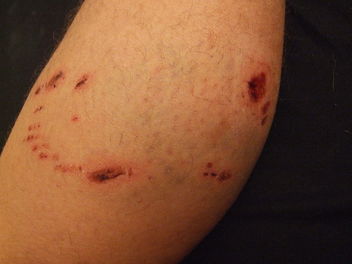
 Dog Bite
Dog Bite
There are however specific dog breeds which are most responsible for dog bites leading to death or dis-figuration. Statistics have shown that dogs such as, rottweilers, pit bulls, presa canarios, mastiffs cane corsos, dogo argentinos, boxers, fila brasieros, sharpeis and mixes of these animals inflict the following:
- 86% of attacks that induce bodily harm
- 81% of attacks to children
- 89% of attack to adults
- 76% of attacks that result in fatalities
- 86% that result in maiming
- Embody 9.2%+ of the total dog population
- Examining The Bite
- cleaning the wound
- Applied antibiotic
- Dressing
There are however many persons who have been bitten by dogs with less severe injuries and choose to doctor themselves without visiting a licensed and experience doctor. So if you are one of those persons who want to treat the dog bite yourself you will need to do so immediately after the bite and simply apply these steps for proper dog bite wound care protocol.
- Clean the bitten area with clean water
- Then use antiseptic (hydrogen peroxide) to clean the wound.
- Apply Iodine to the affected areas. Iodine can kill fungus, bacteria, and other microorganisms such as amoebas.
- Dress wound and periodically redress and apply iodine after redressing.

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed



